Understanding the technology behind PCB’s in Household Boilers
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are the backbone of modern electronic devices, including household boilers, serving as the foundation upon which all electronic components are mounted. From simple heating systems to complex boiler management systems, PCBs are integral to the functionality and reliability of these systems. Understanding the technology behind PCBs is essential for anyone involved in electronics, whether as a hobbyist, engineer, or manufacturer. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of PCB technology as it relates to household boilers, exploring its components, manufacturing processes, and applications.
The Basics of PCB Technology in Boilers
What is a PCB?
A Printed Circuit Board is a flat board made from non-conductive materials, such as fibreglass, composite epoxy, or other laminate materials. It supports and electrically connects electronic components using conductive pathways, tracks, or signal traces etched from copper sheets laminated onto a non-conductive substrate. In household boilers, PCBs can be single-sided, double-sided, or multi-layered, depending on the complexity and requirements of the heating system.
PCBs are crucial in boilers because they provide a compact and organised way to integrate various electronic components, such as sensors, relays, and control units, into a single unit. This integration not only saves space but also enhances the system’s performance and reliability.
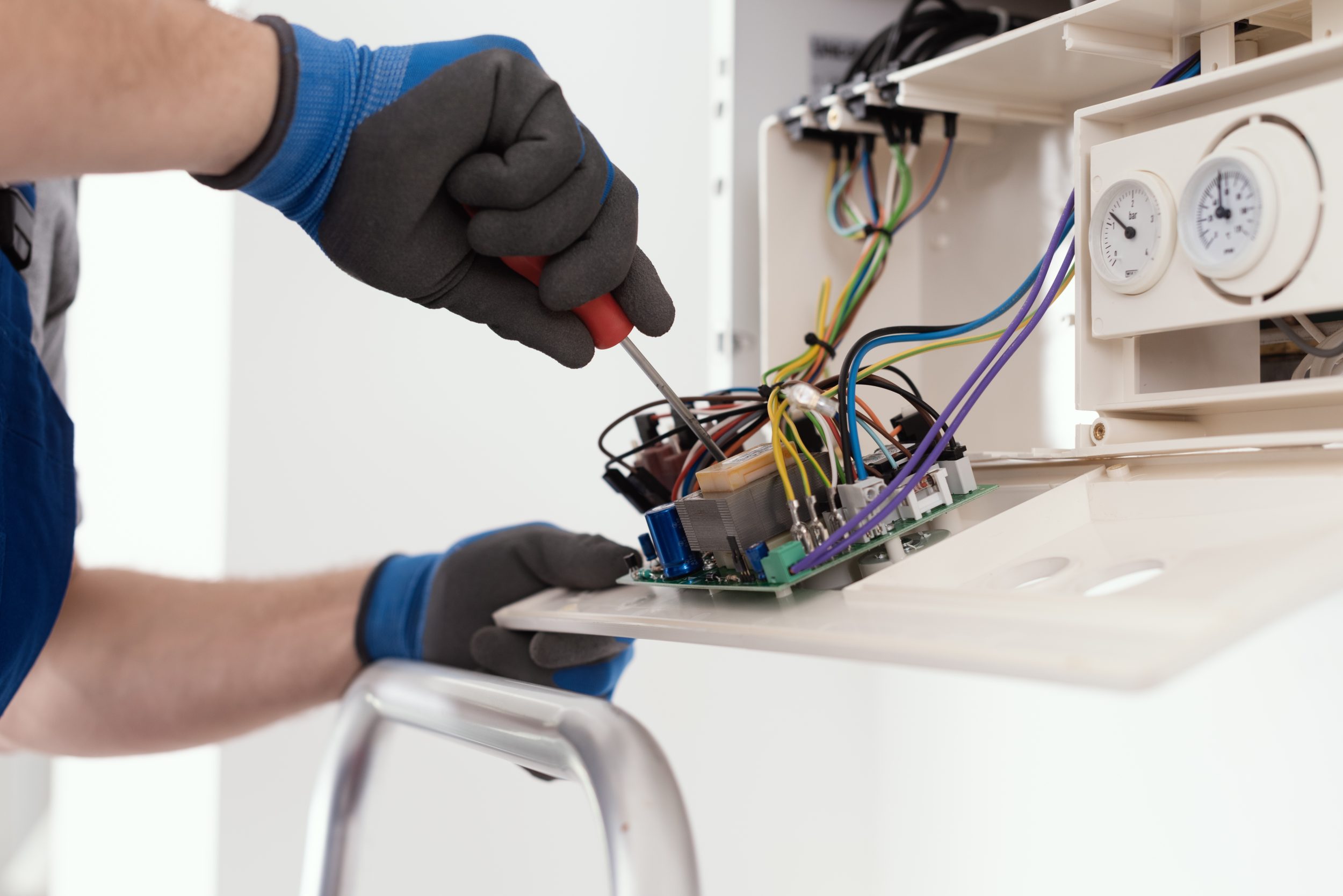

Components of a PCB in Boilers
PCBs in household boilers consist of several key components, each playing a vital role in the board’s functionality. The substrate, typically made of fibreglass, provides the board’s structural integrity. Copper layers are etched to create the circuit paths, allowing electrical signals to travel between components. The solder mask, a protective layer, prevents short circuits and protects the copper traces from environmental damage, which is particularly important in the humid environment of a boiler.
Silkscreen is another component of PCBs, used to print labels and symbols on the board, aiding in the identification and assembly of components. The combination of these elements results in a robust and efficient platform for the electronic circuits that control household boilers.
PCB Manufacturing Process for Boilers
Design and Layout
The manufacturing process of a PCB for a household boiler begins with its design and layout, which is typically done using specialised software. Engineers create a schematic diagram that outlines the electronic circuit, followed by a layout design that specifies the physical arrangement of components and traces on the board. This step is crucial, as it determines the board’s functionality and performance in controlling the boiler’s operations.
Design considerations include the board’s size, the number of layers, and the placement of components. Engineers must also account for factors such as signal integrity, thermal management, and electromagnetic interference to ensure optimal performance in the boiler’s environment.
Fabrication
Once the design is finalised, the fabrication process begins. This involves creating the physical board by layering and etching copper sheets onto the substrate. The fabrication process includes several steps, such as drilling holes for component leads, applying solder mask and silkscreen, and cutting the board to its final dimensions.
Advanced techniques, such as photolithography and chemical etching, are used to create precise circuit patterns. The fabrication process requires meticulous attention to detail to ensure the board meets the design specifications and functions correctly within the boiler system.
Assembly and Testing
After fabrication, the PCB undergoes assembly, where electronic components are mounted onto the board. This can be done using through-hole technology, where component leads are inserted into drilled holes, or surface-mount technology, where components are soldered directly onto the board’s surface.
Once assembled, the PCB is subjected to rigorous testing to verify its functionality and performance. Testing methods include visual inspection, electrical testing, and functional testing to ensure the board operates as intended in controlling the boiler. Any defects or issues are addressed before the board is integrated into the final product.
Applications of PCBs in Household Boilers
Control Systems
PCBs are ubiquitous in household boilers, powering control systems that manage heating, temperature regulation, and safety features. Their compact size and ability to integrate multiple components make them ideal for modern boiler systems, where space and efficiency are paramount. PCBs enable the seamless operation of these systems, providing the necessary connections and pathways for electrical signals.
The versatility of PCBs allows for the development of increasingly sophisticated and feature-rich boiler control systems, driving innovation and enhancing user experiences.
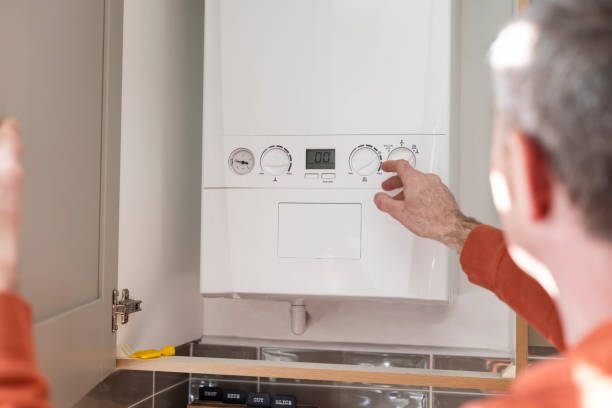

Safety Features
In household boilers, PCBs play a crucial role in the operation of various safety systems, including pressure controls, temperature sensors, and emergency shut-off mechanisms. As boilers become more technologically advanced, the demand for reliable and efficient PCBs continues to grow. PCBs are essential for the integration of electronic components that enhance boiler performance, safety, and user comfort.
With the rise of smart home technology, PCBs are becoming even more critical, supporting the complex electronic systems required for these cutting-edge boiler technologies.
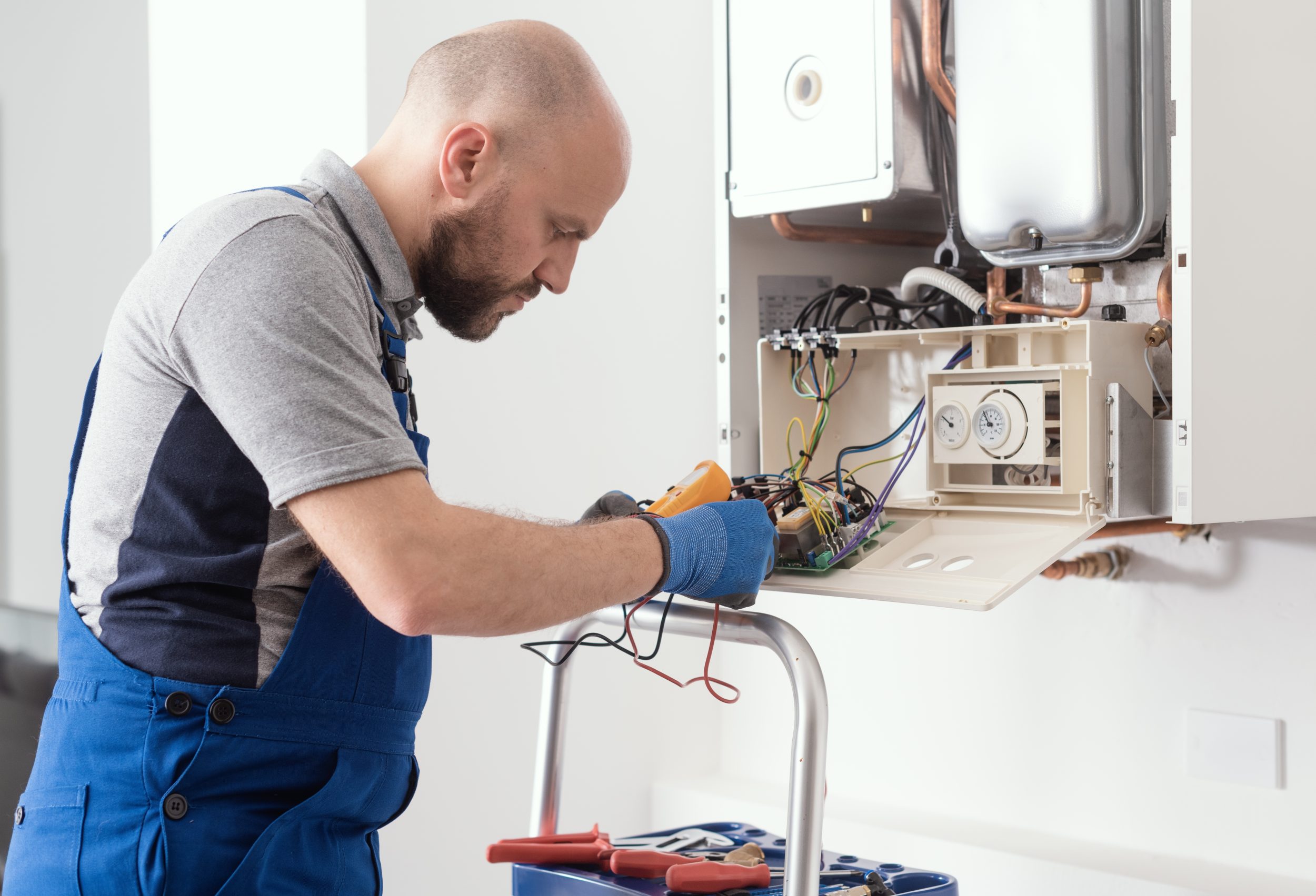

Energy Efficiency
PCBs are also vital in the development of energy-efficient household boilers, where they are used in control systems that optimise fuel consumption and reduce emissions. The precision and reliability of PCBs are crucial in these applications, where accuracy and dependability can significantly impact energy savings and environmental sustainability.
Advancements in PCB technology have enabled the development of smarter, more efficient boiler systems, improving energy management and expanding the possibilities for sustainable heating solutions.
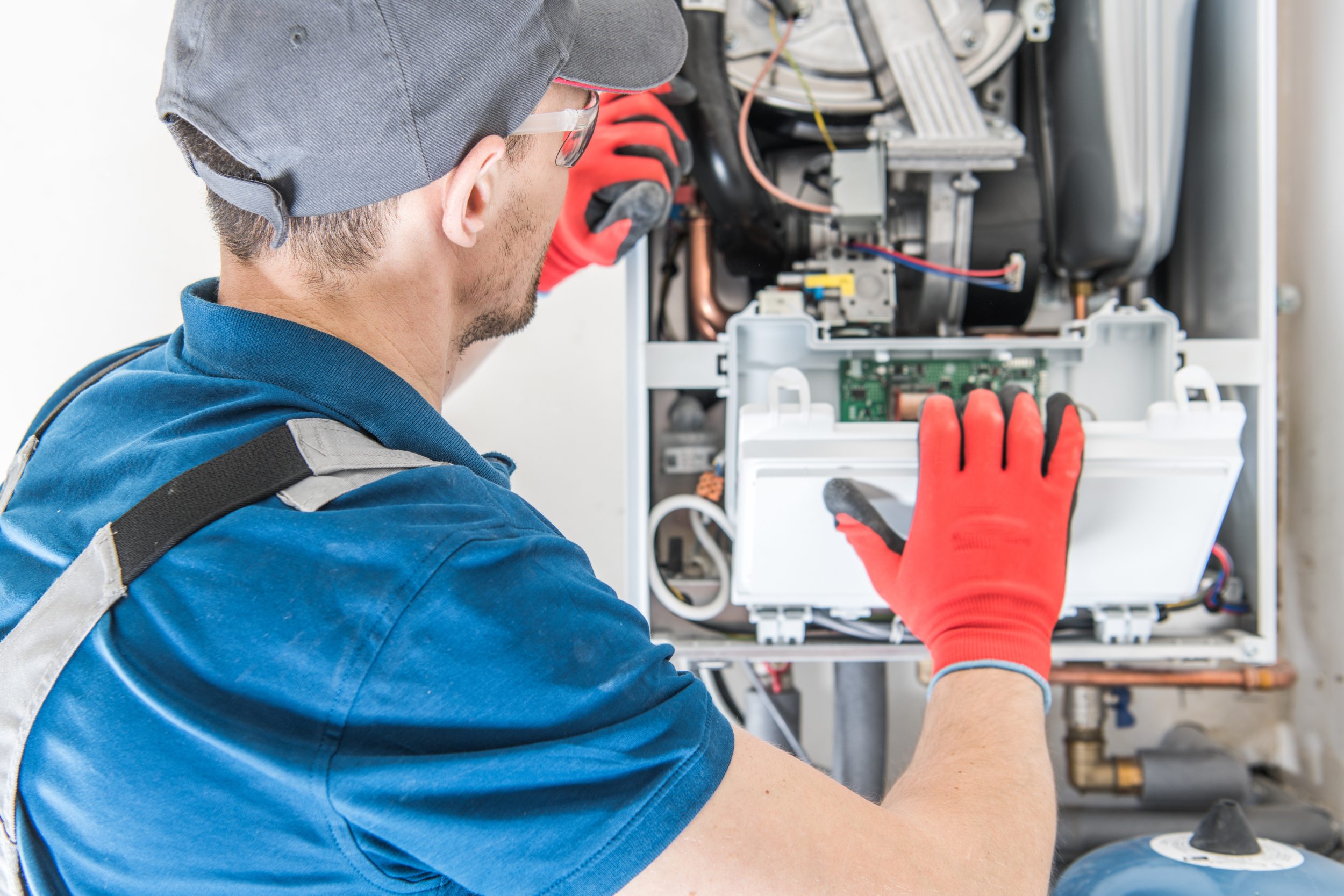

Future Trends in PCB Technology for Boilers
Miniaturisation and Flexibility
As technology continues to evolve, the demand for smaller and more flexible PCBs in household boilers is increasing. Miniaturisation allows for the development of compact electronic control systems, while flexible PCBs offer new possibilities for design and application in tight spaces. These trends are driving innovation in PCB manufacturing, with new materials and techniques being developed to meet the growing demand.
Flexible PCBs, in particular, are gaining popularity due to their ability to conform to various shapes and sizes, making them ideal for boiler systems where traditional rigid PCBs are not suitable.
Environmental Considerations
With increasing awareness of environmental issues, the PCB industry is focusing on sustainable practices and materials, particularly in the context of household boilers. Efforts are being made to reduce waste, improve recycling processes, and develop eco-friendly materials that minimise environmental impact. These initiatives are essential for the long-term sustainability of the PCB industry and the heating sector as a whole.
Innovations in green technology are also influencing PCB design and manufacturing, with a growing emphasis on energy efficiency and reduced carbon footprints in boiler systems.
Advanced Materials and Techniques
The development of advanced materials and manufacturing techniques is shaping the future of PCB technology in household boilers. New materials, such as high-frequency laminates and advanced composites, are being used to enhance the performance and capabilities of PCBs. These materials offer improved thermal management, signal integrity, and durability, meeting the demands of increasingly complex boiler systems.
Innovative manufacturing techniques, such as additive manufacturing and 3D printing, are also being explored to improve efficiency and reduce costs in PCB production for boilers. These advancements are paving the way for the next generation of heating devices, offering new possibilities for design and functionality.
In conclusion, understanding the technology behind PCBs is crucial for navigating the ever-evolving landscape of household boilers. From their basic components to advanced manufacturing processes and applications, PCBs are a fundamental aspect of modern heating technology, driving innovation and shaping the future of boiler systems.


